品牌:德国肖特生物芯片(SCHOTT)NEXTERION®
规格:75.6mm*25mm
厚度:1.0mm
起订:25件
发货:3天内
Aminosilane coating 氨基硅烷涂层
NEXTERION® Slide A+
Aminosilane coated slides remain the most popular choice for printing PCR products, and long oligonucleotides, despite the emergence of innovative three-dimensional microarray surfaces, and other “active” surface chemistries such as epoxysilane. With it's NEXTERION®Slide A+ SCHOTT is committed to providing the best aminosilane microarray slides on the market.
Overview
|
Type of coating |
Immobilization method |
Typical probes |
Ordering information |
|||
|
NEXTERION®product |
Barcode option |
Item number |
Slides per pack |
|||
|
Aminosilane |
Ionic interaction followed by cross-linking via an additional UV or baking step |
• Long oligonucleotides |
Slide A+ |
None |
1064875 |
25 |
|
Laser |
1064877 |
25 |
||||
|
Key product features |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Printed slides have a long shelf life |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Compatible with a wide range of spotting buffers |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Coatings with uniform aminosilane density |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Regular spot uniformity and morphology |
|
Typical applications |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• ArrayCGH |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Transcriptional profiling |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• SNP genotyping |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Splice variant detection |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• DNA methylation profiling |
|
Suitable probe types |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• BACS or PACs |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Oligonucleotides ≥ 40 mers |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Small protein fragments such as peptides |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• cDNA |
Introduction
Aminosilane surfaces provide available amine groups for initial ionic attachment of the negatively charged phosphate groups in the DNA backbone. Conventional wisdom is that longer aminosilane molecules with multiple amino groups produce higher signal-to-background ratios, as their higher positive charge will bind more DNA to the slide surface. However, recent research at SCHOTT has shown that the situation is actually more complicated than this, and that while surfaces with a higher charge do bind more DNA, they are also more difficult to block effectively, resulting in significantly higher non-specific binding. The higher levels of non-specific binding have a negative effect leading to poorer signal-to-background ratios.
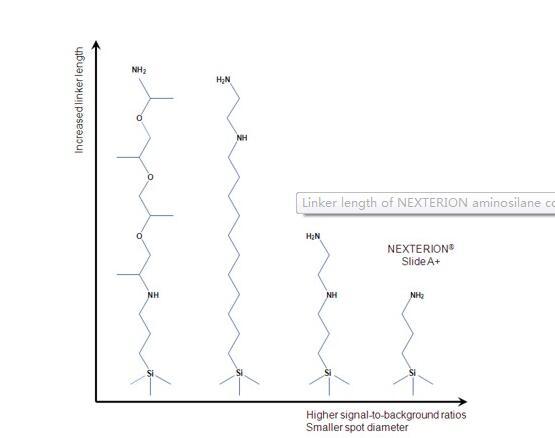
Comparison of aminosilane structures
The aminosilane slide offered by SCHOTT is based on very short chain aminosilanes that demonstrate high signal intensities, and exceptionally low background signals, when compared with other commercially available aminosilane slides.

Immobilization chemistry
Aminosilane coated slides have a high concentration of primary aminogroups available at the surface. These groups become protonated and therefore positively charged when placed in contact with a near-neutral, aqueous solution. Negatively charged probe molecules, such as DNA, will initially form multiple ionic interactions with the positively charged amino surface coating. Additional amino-modifications of the nucleic acids are not required, but such modifications do not interfere with the immobilization. After spotting, the probes are covalently linked to the slide surface by either heating, or a brief exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. Other types of negatively charged biomolecules may also be coupled to aminosilane surfaces.

SCHOTT slides are manufactured from a high quality, low intrinsic fluorescence borosilicate glass. The glass slides are cleaned and coated in a class 100, environmentally controlled clean room to ensure contamination and artifact free surfaces. The aminosilane coatings are applied using a unique, and innovative method developed and optimized by SCHOTT, that allows the production of large lot sizes with excellent intra-lot, and inter-lot reproducibility. Each slide lot is tested using both physical and functional quality control checks. The density of the aminosilane groups in the coatings remain uniform over the entire surface of the slides, and is optimized to maximise the DNA binding capacity. The surface hydrophobicity is tightly controlled to optimize the performance with both contact and non-contact microarray printers. The Slide A+ surface is more hydrophobic than the AStar surface, resulting in smaller spots, making it ideally suited for printing higher density arrays.
NEXTERION® Slide A+, and Slide AStar are compatible with the most commonly used aminosilane protocols and a wide range of spotting buffers. This makes it easy to evaluate and switch to the NEXTERION® aminosilane slides from competitor slides.
Selecting the most suitable NEXTERION® aminosilane coating
Choosing the best SCHOTT aminosilane slide for the application depends on a number of factors. One important factor is the buffer used for printing the arrays. SCHOTT has developed a printing buffer system (NEXTERION® Spot A HD) for printing high-density arrays of up to 50k spots on the SCHOTT aminosilane slides. The buffer system is designed to minimize sample evaporation during long print runs.

Packaging and storage
Format
NEXTERION® Slide AStar and A+ are available in packs of 25-slides with optional code 128 barcodes enabling automated sample tracking. The AStar and A+ aminosilane coating are also available in 16-well slide, 48-well slide and 96-well microplate formats. For further information refer to the section on “Multi-well formats”.














